Introduction:
Microwave ovens are those magical boxes that turn cold leftovers into hot meals in just a few minutes. We’ve all used them, especially when we wanted something to eat late at night or when we weren’t very good at cooking. But have you ever thought about how does a microwave works to heat foods?
This article goes into great detail about the science behind microwaves. It talks about how microwave ovens work, who made them, how microwave radiation affects food, and whether or not microwaves are safe.
What Is a Microwave? Definition and Meaning
A microwave is a type of electromagnetic wave that has a wavelength between one millimetre and one metre and a frequency between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). Like visible light, infrared, and radio waves, microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation, but they have a shorter wavelength.
Microwaves are used in more than just cooking. They are also used in radar systems, satellite communications, and medical imaging.
The frequency of microwave waves used for heating food typically falls around 2.45 GHz, which is a range that gets water molecules excited.
The Invention of the Microwave Oven
The microwave oven is an example of a scientific discovery that came about by accident and curiosity.
Percy Spencer, an engineer at Spencer Appliances (Raytheon), was testing a magnetron in 1945. This device made microwaves for radar systems during World War II.
He saw that a chocolate bar in his pocket melted while he was standing near an active magnetron. Spencer was interested, so he started to experiment by putting popcorn kernels and an egg near the magnetron. The egg exploded and the popcorn popped right away.
That moment led to one of the best inventions for the home in modern history. Spencer figured out that microwave radiation could quickly heat food.
The first microwave oven, called the Radarange, was sold to the public in 1947. It was huge, over 5 feet tall and weighing about 750 pounds. The first microwave oven cost a lot of money and was mostly used in restaurants and factories.
In the 1960s and 1970s, microwave ovens got smaller, cheaper, and better at cooking. They were common household items by the 1980s.
What are The Components Used in Microwave Oven?
Lets Understanding the vital components of a microwave oven and their roles in the cooking process:
Internal Components (Inside the Oven):
High Voltage Transformer:
- Microwaves demand high voltage (usually 3000 to 4000 volts) to function and heat food.
- As standard power outlets provide only 115 volts, a transformer converts the voltage to a higher level.
Magnetron:
- The magnetron is crucial, converting high-voltage electricity into microwave energy.
- Utilizing a specially designed diode and magnetic fields, the magnetron controls electrons to create microwaves.
Waveguide:
- A hollow metal tube guides and directs microwaves produced by the magnetron.
- Reflective inner walls ensure microwaves stay within the cooking cavity, enhancing safety.
Cooling Fan or Stirrer:
- To prevent overheating, microwaves include a cooling fan or stirrer fan.
- The cooling fan dissipates oven heat, maintaining a safe temperature.
Cooking Cavity:
- The cooking cavity is where food is placed for heating or cooking.
Turntable:
- Many microwaves feature a rotating turntable inside the cooking cavity.
External Components (Not Inside the Oven):
Power Cord:
- Connect the microwave to the electrical outlet.
Control Panel:
- Allows users to set cooking times, power levels, and other settings.
Door:
- Provides access to the cooking cavity with safety mechanisms to prevent operation when open.
Remember, these components work harmoniously to create the magic of microwave cooking!
How do microwaves work?
Let’s look at the science behind how microwaves work to learn more.
A magnetron is a type of vacuum tube that turns electricity into electromagnetic microwaves. It is an important part of every microwave oven. These microwaves go into the microwave cavity, where they bounce around and get into the food.
This is what happens step by step:
- Microwave Generation: The magnetron makes electromagnetic waves with a frequency of about 2.45 GHz.
- Distribution of Energy: These waves go into the cooking chamber and bounce off the metal walls, making sure that the energy is spread out evenly.
- How Microwaves Affect Food: Microwaves make polar molecules, especially water, vibrate very quickly, usually billions of times per second.
- How to Make Heat: Dielectric heating uses this molecular vibration to make heat, which warms the food from the inside out.
That’s why food cooks so quickly in a microwave oven, which uses conduction and convection instead of heat.
Also read – How Does a Camera Capture and Record Images?
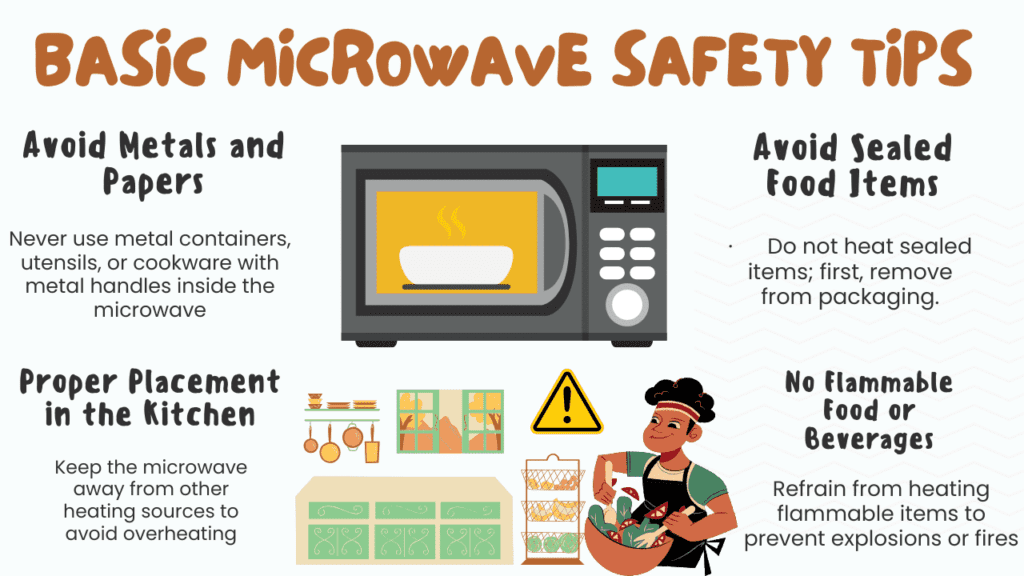
Most Essential Safety Precautions for Microwave Use
Ensuring safety while using microwaves requires these precautions:
Avoid Metals and papers.
- Never use metal containers, utensils, or cookware with metal handles inside the microwave.
- Remove aluminum foil from food before heating.
- Avoid using paper cups or utensils for cooking.
No Flammable Food or Beverages:
- Refrain from heating flammable items to prevent explosions or fires.
Avoid Sealed Food Items:
- Do not heat-sealed items; first, remove from packaging.
Proper Placement in the Kitchen:
- Keep the microwave away from other heating sources to avoid overheating.
Uncover the Vent and Avoid Metal Foil:
- Do not cover the vent during use.
- Avoid covering any part of the microwave with metal foil.
Never Use the Microwave with the Door Open:
- Always ensure the door is securely closed before use.
Immediate Action in Case of Fire:
- Turn off power, unplug, and keep the door closed if a fire occurs.
Common Misconceptions About Microwaves Cooking
Let’s clear up some common misunderstandings about cooking with a microwave:
Radiation leakage
- Myth: People often worry that microwaves leak harmful radiation.
- Fact: Microwaves use a type of radiation called non-ionizing radiation to cook food. Unlike ionizing radiation (like x-rays), which can be harmful, non-ionizing radiation is like what your TV or radio emits. It does not cause cancer, and the waves stay safely within the microwave’s metal walls and windows. So, don’t worry—your microwave won’t give you cancer!
Nutrient loss
- Myth: Some people believe that microwaving food causes significant nutrient loss.
- Fact: While all cooking methods can lead to some nutrient loss, microwaving is generally gentler than others. It preserves more nutrients compared to boiling or frying. So, your microwave isn’t secretly zapping away vitamins—it’s a safe way to cook!
Radiation effects on food
- Myth: Microwaving makes food radioactive.
- Fact: Not true! Microwaves heat food by exciting water molecules, not by making it radioactive.
Which Cookware / Utensil is Best for Microwave Cooking?
-
Glass Containers:
- Excellent for microwave cooking, safe, non-reactive, and can withstand high temperatures.
- Opt for glass containers with microwave-safe lids for reheating or direct cooking.
-
Ceramic Dishes:
- Microwave-safe, but ensure glaze or paint used is also microwave-safe.
- Avoid dishes with metallic accents to prevent sparks.
-
Microwave-Safe Plastics:
- Use plastics labeled as microwave-safe, with a squiggly line symbol at the bottom.
- Avoid regular plastics to prevent melting or releasing harmful chemicals.
-
Silicone Utensils:
- Microwave-safe and flexible, suitable for various cooking needs.
- Check the manufacturer’s instructions for temperature limits.
-
Avoid Metal and Foil:
- Never use metal utensils or containers to prevent sparks and microwave damage.
- Remove metal twist ties or staples from food packaging before microwaving.
-
Stainless Steel:
- Generally safe but not ideal for microwave cooking.
- Ensure it doesn’t touch the microwave’s sides.
-
Microwave-Safe Covers and Lids:
- Use microwave-safe covers to prevent splatters.
- Options include glass lids, microwave-safe plastic covers, or paper towels.
Follow these guidelines for safe and efficient microwave cooking. Enjoy your meals!
Pros and Cons of Microwave Cooking Technology
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of microwave technology:
Advantages of Microwave Cooking Technology:
Speed and Efficiency:
- Enables rapid cooking, saving time in busy lifestyles.
Energy Efficiency:
- Targets water molecules directly, reducing energy wastage.
Preservation of Nutrients:
- Shorter cooking times and lower temperatures preserve nutritional content.
Versatility:
- Effective for reheating, defrosting, and various cooking tasks.
Even Heating with Turntable:
- Turntables promote even heating, minimizing hotspots.
Disadvantages of Microwave Cooking Technology:
Uneven Heating in Some Cases:
- Certain foods or containers may result in uneven cooking.
Limited Browning and Crisping:
- Challenges achieving browning or crisping effects.
Restrictions on Cookware:
- Requires microwave-safe containers, limiting cookware options.
Potential Loss of Textural Quality:
- Some foods may experience texture changes during microwave cooking.
Safety Concerns:
- Safety features notwithstanding, concerns exist, emphasizing the need for regular maintenance.
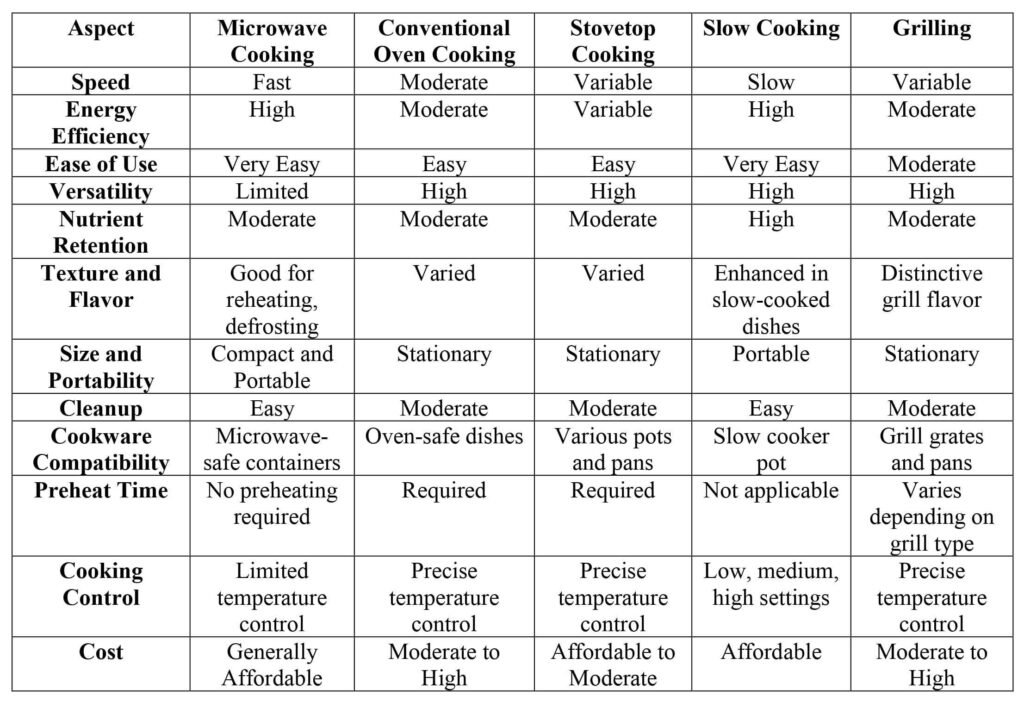
A Comparative Guide: Microwave Cooking vs. Other Cooking Methods
Explore the differences between microwave cooking and other cooking methods:
Keep in mind that the effectiveness of each cooking method depends on the specific dish and personal preferences.
Real-World Applications of Microwaves
Microwave technology extends far beyond cooking. Here are some fascinating real-world applications:
Radar Systems:
Microwaves are used in radar for aircraft navigation, weather forecasting, and speed detection.Telecommunications:
Microwaves carry mobile phone and television signals over long distances.Medical Applications:
Used in diathermy treatments for deep tissue heating and in medical imaging systems.Industrial Processing:
Microwaves are used to dry materials, cure rubber, and even process ceramics.Space Communication:
Satellites use microwave bands to transmit data between Earth and orbiting spacecraft.Mobile Microwave Ovens:
Portable microwave models, known as mobile microwave ovens, are now designed for vehicles and outdoor use.
Conclusion:
In Summary “How Does a Microwave Oven Heat Food?” helps you to understand the complicated science and safety steps involved in this amazing kitchen appliance. With this knowledge, you can make the most of your microwave cooking adventures.
Remember: Microwaves are not just for reheating – they’re also time machines that transport you from hunger to satisfaction in seconds!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This FAQ section is designed to provide quick and clear answers to the most common inquiries we receive. We encourage you to click on a question to find the information you need. If you can’t find an answer here, please don’t hesitate to visit our Contact Us page for further assistance.
Who invented the microwave oven?
Percy Spencer, an engineer at Raytheon (Spencer Appliances), invented the microwave oven in 1945.
When was the microwave invented?
The discovery was made in 1945, and the first commercial oven appeared in 1947.
How does a microwave oven work?
It uses a magnetron to generate electromagnetic waves that excite water molecules in food, creating heat through molecular vibration.
Are microwave ovens safe?
Yes, they are non-ionizing and safe when used properly.
What is microwave radiation?
Microwave radiation is non-ionizing electromagnetic energy used for heating, radar, and communication.
What is the frequency of microwave waves?
Microwave ovens operate around 2.45 GHz frequency.
Can microwaves give you cancer?
No evidence supports that properly used microwave ovens cause cancer.
How long do microwaves last?
Typically between 7 to 10 years.
Who made the first microwave oven?
Raytheon Company, under the guidance of Percy Spencer.
What is the wavelength of microwaves?
Around 12 centimeters in common microwave ovens.
Having any queries? – Do reach us at info@scivoyage.com