Introduction:
Using sunscreen is an excellent strategy to protect your skin if you spend time outside in the sun, but How Does Sunscreen Work to Protect Your Skin from UV Rays?
Dermatologists, chemists, and people who love skincare have been interested in this question for decades. EltaMD sunscreen, tinted sunscreen, and reef-friendly sunscreen are all examples of sunscreens that use scientific formulas to block, reflect, or absorb UV radiation. They act like an invisible shield for your skin.
We’ll talk about the science behind sunscreen, what it’s made of, what SPF (Sun Protection Factor) means, and how to choose the best sunscreen for kids, oily skin, and sensitive skin in this article.
What are the sunscreens?
Sunscreens are creams or lotions that you put on your skin to protect it from harmful UV rays. Chemical filters or mineral agents are examples of active ingredients that absorb, scatter, or reflect UV light before it gets into the skin.
You can find sunscreen in a lot of different forms these days, like sunscreen lotion for tattoos, tinted mineral sunscreen, sunscreen stick, body sunscreen, or spray sunscreen for face. Each type is made to fit your skin type, activity level, and ease of use.
New products like reef-friendly sunscreen, pregnancy-safe sunscreen, and non-comedogenic sunscreen have made it easier to take care of your skin while also being safe for the planet.
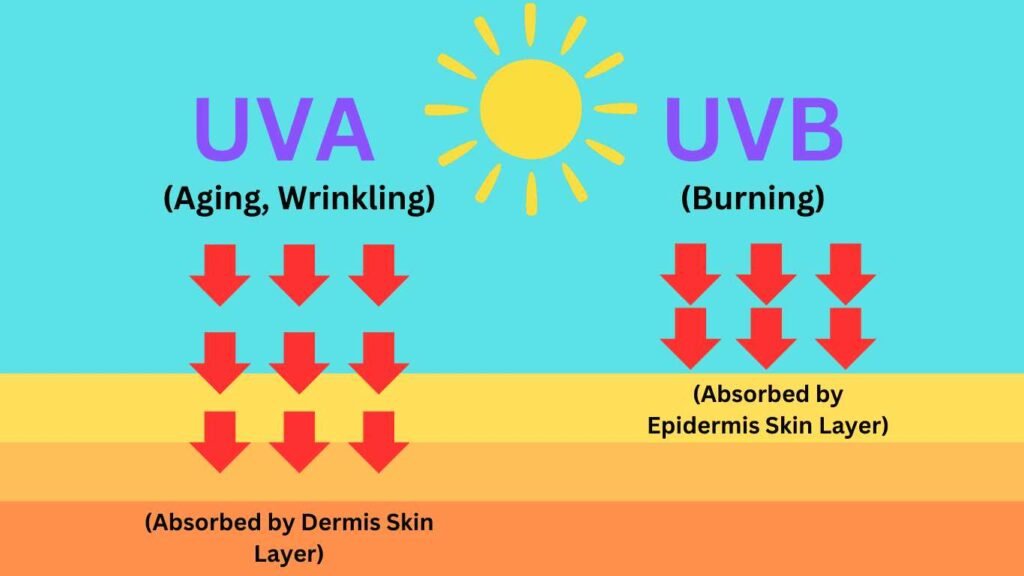
Understanding UV Rays: UVA and UVB
There are two main kinds of UV radiation in sunlight that can harm the skin:
- UVA rays go deep into the skin and cause wrinkles, premature aging, and long-term damage.
- UVB rays cause sunburn and are a direct cause of skin cancer.
Dermatologists suggest broad-spectrum sunscreens like Anessa sunscreen, La Roche-Posay mineral sunscreen, and Heliocare sunscreen cream. These protect against both UVA and UVB rays.
Also, UVA photons are absorbed more deeply by the skin, which makes wrinkles and other signs of early skin aging more likely to happen. There are about 500 times more UVA photons in sunlight than UVB rays.
The Science of How Sunscreen Works
When you put on sunscreen, it makes a thin layer of protection on your skin. Depending on how it is made:
- Chemical sunscreens, such as Biore sunscreen or Isntree sunscreen, soak up UV rays and change them into heat that is safe through a chemical reaction.
- Mineral or physical sunscreens, such as those made with titanium dioxide or zinc oxide, reflect and scatter UV light away from the skin.
This two-part system keeps your skin safe whether you’re swimming, hiking, or just enjoying a sunny day.
Some more advanced sunscreens, like Alastin tinted sunscreen and Beauty of Joseon sunscreen, have antioxidants and hydrating agents in them to fight free radicals and dryness that can happen when you’re in the sun.
What Does SPF Mean?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor measures how effectively a sunscreen protects against UVB rays.
For instance:
- SPF 15 blocks about 93% of UVB rays.
- SPF 30 blocks about 96%.
- SPF 50 blocks about 98%.
A higher SPF doesn’t mean you can stay outside forever; it just means your skin will start to burn later. No matter what SPF level you use, whether it’s SPF 30 sunscreen or SPF 100 sunscreen, you need to reapply it.
The Role of SPF in Skin Protection
Regular use of SPF products reduces the risk of:
- Sunburn
- Skin cancer
- Premature aging
- Pigmentation and brown spots
Dermatologists suggest reapplying sunscreen every two hours, especially after sweating or swimming. Even water resistant sunscreen like EltaMD sunscreen tinted and Anua sunscreen can lose effectiveness over time.
Types of Sunscreen: Mineral vs. Chemical
There are three main types of sunscreen — Mineral (Physical), Chemical, and Hybrid (Tinted) — each working differently and suited for specific skin needs.
Mineral Sunscreens
This is also known as physical sunscreens, reflect UV rays using active ingredients like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide.
- They are ideal for sensitive skin, children, and those with eczema-prone skin.
- Popular examples include Blue Lizard sunscreen, Thinkbaby sunscreen, EltaMD sunscreen, and Tizo sunscreen.
Chemical sunscreens
Chemical sunscreens work by absorbing UV rays and then releasing the energy as heat.
- These are best suited for people with oily or combination skin, as they tend to feel lighter and absorb quickly without leaving a white cast.
- Common examples include Biore UV sunscreen, Isntree sunscreen, and Neutrogena sunscreen spray.
Hybrid (Tinted) Sunscreens
Hybrid (Tinted) Sunscreens combine both mineral and chemical filters to provide balanced protection and a more natural finish.
- They’re ideal for makeup users and for daily wear, as they often include skin-tone tints that even out complexion.
- Popular choices include Tinted sunscreen, Alastin tinted sunscreen, and Live Tinted sunscreen.
Different SPF products for your skin type:
- SPF 15: Blocks approximately 93% of UVB rays. Proper for cloudy days or indoor adventures.
- SPF 30: Shields around 96% of UVB rays. Best for seashore escapades and picnics.
- SPF 40: Shields around 97% of UVB rays. Best for Hiking and Trekking and Outdoor Sports.
- SPF 50: Shields around 98% of UVB rays. Best for extended outdoor activities.
- SPF 50+: Fends off 99 % of UVB rays. Ideal for tropical expeditions and sun-soaked afternoons.
Keep in mind that SPF only indicates how much UV radiation is blocked; it doesn’t tell you how long you are allowed to stay in the sun. All areas of your skin that are exposed to the sun should have sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, regardless of your skin type.
Classification of Different Skin Types:
The Fitzpatrick skin typing system is a way to classify skin types based on specific features and their risk of sunburn and skin cancer. It defines six different skin types based on melanin content and sun sensitivity:
- Type 1: Very pale skin, often with light blue, grey, or green eyes, and fair or red hair. Burns easily and rarely tans.
- Type 2: Pale pink or beige skin, blue, gray, green, or hazel eyes, and blond or brown hair. Burns easily and tans with difficulty.
- Type 3: Pink or medium-beige skin, brown or dark-blue eyes, and dark blond, brown, or black hair. Sometimes burns and tans slowly.
- Type 4: Olive or light-brown skin, dark brown eyes, and dark-brown or black hair. Rarely burns and tans with ease.
- Type 5: Medium to dark-brown skin, dark brown eyes, and dark brown or black hair. Burns very rarely and tans readily.
- Type 6: Deep dark-brown or black skin, very dark eyes, and black hair.
How to Choose the Right Sunscreen for Your Skin Type
1. For Sensitive Skin
Opt for fragrance-free, non-comedogenic sunscreen like best sunscreen for sensitive skin or Avene sunscreen. Products like Babo Botanicals sunscreen or EWG sunscreen guide-approved brands are gentle yet effective.
2. For Oily or Acne-Prone Skin
Lightweight, oil-free formulas like best sunscreen for acne prone skin or Neutrogena Hydro Boost sunscreen prevent clogged pores while keeping shine under control.
3. For Dry Skin
Hydrating options like tinted mineral sunscreen or Biore Aqua sunscreen provide moisture with UV protection.
4. For Kids
Look for best sunscreen for kids or Baby Bum sunscreen, which are mild, tear-free, and free from harsh chemicals.
5. For Outdoor and Water Sports
Athletes and swimmers should choose sport sunscreen, waterproof sunscreen, or reef friendly sunscreen options like Sun Bum sunscreen and ThinkSport sunscreen reef safe.
Also read – How Does a Camera Capture and Record Images?
Sunscreen Application Tips & Common Mistakes
When people use sunscreen, many forget to apply enough sunscreen, which reduces its effectiveness. Follow these guidelines:
- Every 2 hours: Reapply your sunscreen every 2 hours, even on cloudy days when sneaky UVB rays are still around.
- After swimming or sweating: Reapply your sunscreen as water can wash away its protection.
- Cover all bases: Make sure to cover all areas, including your ears, lips, and other sensitive areas that need SPF protection.
- The Waiting Period: Wait for 15 to 30 minutes after applying sunscreen to dry skin before going outdoors. This allows the sunscreen to be absorbed properly.
- Don’t forget sensitive spots: ears, scalp, lips (use SPF lip sunscreen), and neck.
- Don’t forget to put on sunscreen before or after moisturiser. Always put sunscreen on after moisturiser to make the last layer of protection.
Even the best Korean sunscreen or Japanese sunscreen won’t help if it’s applied incorrectly or too little.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sunscreen
Advantages
- Shields against sunburn and skin cancer.
- Prevents premature aging and sunspots.
- Maintains even skin tone and reduces pigmentation.
- Protects tattoos with sunscreen lotion for tattoos.
- Reduces sun-triggered allergies and rashes.
Disadvantages
- Some people experience skin allergies or irritation.
- Overuse can slightly reduce vitamin D production.
- Certain chemical sunscreens may affect coral reefs, making reef safe sunscreen a better option.
- Poor-quality products may clog pores, especially in humid conditions.
Also read – How Does a Microwave Work to Heat Food?
Conclusion: A Shield from the Sun
When you know how sunscreen protects your skin from UV rays, you can make smart choices about how to care for your skin. The science is the same for all types of sunscreen, from EltaMD sunscreen to Biore sunscreen, and from best sunscreen for sensitive skin to reef friendly sunscreen. It protects by absorbing, reflecting, and preventing.
Sunscreen is like armour for your skin. It’s something you should do every day to stay healthy, beautiful, and safe in the sun. The most important thing is to be consistent, whether you choose a tinted sunscreen for everyday use or a sport sunscreen for outdoor activities.
So, wear your sunscreen, trust the science, and enjoy the sun in a safe way.
Disclaimer: Science Voyage’s team SPF knowledge is purely celestial. Consult a dermatologist for earthly advice.
Fequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
This FAQ section is designed to provide quick and clear answers to the most common inquiries we receive. We encourage you to click on a question to find the information you need. If you can’t find an answer here, please don’t hesitate to visit our Contact Us page for further assistance.
Can you tan with sunscreen?
Yes, you can still tan with sunscreen, but the tan will be lighter and slower. Sunscreen filters most of the harmful UVB rays that cause burns but allows a small amount of UVA to reach your skin — that’s what triggers melanin production (tanning). Using sunscreen helps reduce skin damage while still allowing a mild tan to develop safely.
Can sunscreen expire?
Absolutely. Sunscreen can expire, and using expired sunscreen reduces its effectiveness. Most sunscreens have a shelf life of about 3 years. After expiration, the active ingredients like zinc oxide or avobenzone may break down, providing less UV protection. Always check the expiration date on the bottle before applying.
How long does sunscreen last?
On average, sunscreen protection lasts about 2 hours on the skin. However, it can wear off faster due to sweating, swimming, or towel drying. Always reapply sunscreen every 2 hours, or more frequently if you’re outdoors or in water.
Can you still tan with sunscreen?
Yes — even with sunscreen, you can still tan slightly. The tan occurs because no sunscreen blocks 100% of UV rays. For example, an SPF 50 sunscreen filters about 98% of UVB rays, so a small amount still penetrates the skin. That’s enough to stimulate melanin and cause a light tan over time.
When was sunscreen invented?
Modern sunscreen was invented in 1938 by Franz Greiter, an Austrian chemist. He created a product called “Gletscher Crème” (Glacier Cream) to protect against sunburn while climbing. The concept of SPF (Sun Protection Factor) was later developed in the 1960s, revolutionizing sun protection science.
How often to reapply sunscreen?
Dermatologists recommend you reapply sunscreen every 2 hours. If you’re swimming, sweating, or using a towel, reapply immediately afterward — even if you’re using water-resistant sunscreen. Regular reapplication ensures consistent UV protection throughout the day.
Which sunscreen is best for dry skin?
For dry skin, choose a hydrating sunscreen that contains moisturizing ingredients like hyaluronic acid, ceramides, or glycerin. Cream-based formulas work better than gels. Some excellent options include:
- EltaMD sunscreen for dry skin
- La Roche-Posay Anthelios Melt-in Milk Sunscreen
- CeraVe Hydrating Mineral Sunscreen
These not only protect but also nourish and restore skin moisture.
Does sunscreen prevent tanning?
Yes, sunscreen reduces tanning significantly by blocking most UV rays. However, it doesn’t completely prevent it. Higher SPF sunscreens (SPF 50 or more) offer the best protection against tanning, especially for sensitive or fair skin.
Which sunscreen is best for all skin types?
The best sunscreen for all skin types is one that is non-comedogenic, fragrance-free, and broad-spectrum. Good examples include:
- EltaMD UV Clear Broad-Spectrum SPF 46
- Neutrogena Ultra Sheer Dry-Touch SPF 55
- Anessa Perfect UV Sunscreen Skincare Milk
These suit oily, dry, and combination skin equally well.
Which sunscreen is best for combination skin?
For combination skin, use lightweight gel or lotion sunscreens that control oil without drying. Try:
- Biore UV Aqua Rich Watery Essence
- Anessa Sunscreen Gel SPF 50+
- COSRX Aloe Soothing Sun Cream
They balance hydration and oil control, ideal for mixed skin textures.
Can we apply sunscreen at night?
Generally, you don’t need sunscreen at night, as there’s no UV radiation after sunset. However, if your sunscreen has additional skincare benefits like antioxidants, niacinamide, or moisturizing ingredients, you can use it as a night moisturizer. Otherwise, stick to your regular night cream.
Does sunscreen remove tan?
No — sunscreen doesn’t remove tan, but it prevents further tanning and protects the skin from darkening more. To fade an existing tan, combine sunscreen use with exfoliation, vitamin C serums, and moisturizers to encourage skin cell renewal.
What to apply first — moisturizer or sunscreen?
Always apply moisturizer first, then sunscreen last.
Here’s why:
- Moisturizer hydrates your skin and helps it stay smooth.
- Sunscreen forms a protective layer on top to block UV rays.
If you apply sunscreen first, your moisturizer may dilute it, reducing its effectiveness. Wait 2–3 minutes after applying moisturizer before putting on sunscreen.
Having any queries? – Do reach us at info@scivoyage.com













1 thought on “How Sunscreen Protect Skin from UV Rays”
If you would likke to take a good deall from this piede of writing then you have to apply these techniques to your wwon website. http://Boyarka-Inform.com