Introduction:
Microwave ovens are those magical boxes that transform cold leftovers into piping-hot meals in mere minutes. We’ve all relied on them, especially during late-night cravings or when our culinary skills are on vacation. But have you ever wondered how does a microwave works to heat foods?
Buckle up, because in this article, we’ll delve into the science behind microwave ovens and unveil their secrets.
The Basics: Electromagnetic Waves and Water Molecules
Microwaves – The Invisible Kitchen Wizards:
- Microwave ovens utilize microwaves, a form of electromagnetic radiation, to cook food.
- Like waves from TV and radio transmitters, microwaves travel at the speed of light—about 300,000 kilometers (186,000 miles) per second.
- Despite their small size, microwaves, measuring around 12 centimeters or 5 inches long, pack a punch in terms of energy.
How does a Microwaves Work to Heat the Foods?
- Microwaves penetrate food, interacting with its molecules, especially water molecules.
- When microwaves hit water molecules, they induce rapid vibration, generating heat.
- Unlike traditional ovens that heat from the outside, microwaves cook from the inside out, albeit not precisely.
What are The Components Used in Microwave Oven?
Lets Understanding the vital components of a microwave oven and their roles in the cooking process:
Internal Components (Inside the Oven):
High Voltage Transformer:
- Microwaves demand high voltage (usually 3000 to 4000 volts) to function and heat food.
- As standard power outlets provide only 115 volts, a transformer converts the voltage to a higher level.
Magnetron:
- The magnetron is crucial, converting high-voltage electricity into microwave energy.
- Utilizing a specially designed diode and magnetic fields, the magnetron controls electrons to create microwaves.
Waveguide:
- A hollow metal tube guides and directs microwaves produced by the magnetron.
- Reflective inner walls ensure microwaves stay within the cooking cavity, enhancing safety.
Cooling Fan or Stirrer:
- To prevent overheating, microwaves include a cooling fan or stirrer fan.
- The cooling fan dissipates oven heat, maintaining a safe temperature.
Cooking Cavity:
- The cooking cavity is where food is placed for heating or cooking.
Turntable:
- Many microwaves feature a rotating turntable inside the cooking cavity.
External Components (Not Inside the Oven):
Power Cord:
- Connect the microwave to the electrical outlet.
Control Panel:
- Allows users to set cooking times, power levels, and other settings.
Door:
- Provides access to the cooking cavity with safety mechanisms to prevent operation when open.
Remember, these components work harmoniously to create the magic of microwave cooking!
Also read – How Does a Camera Capture and Record Images?
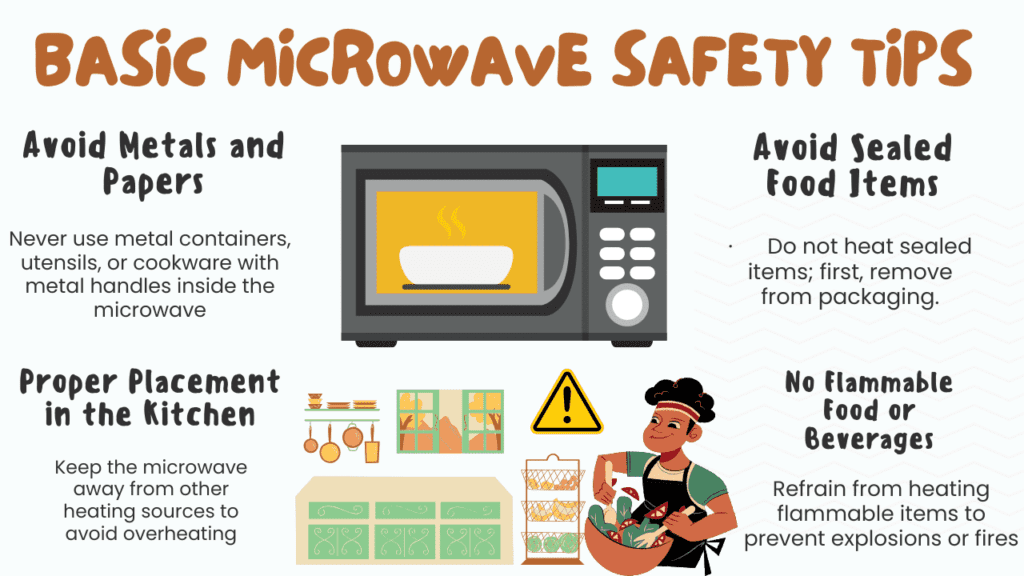
Most Essential Safety Precautions for Microwave Use
Ensuring safety while using microwaves requires these precautions:
Avoid Metals and papers.
- Never use metal containers, utensils, or cookware with metal handles inside the microwave.
- Remove aluminum foil from food before heating.
- Avoid using paper cups or utensils for cooking.
No Flammable Food or Beverages:
- Refrain from heating flammable items to prevent explosions or fires.
Avoid Sealed Food Items:
- Do not heat-sealed items; first, remove from packaging.
Proper Placement in the Kitchen:
- Keep the microwave away from other heating sources to avoid overheating.
Uncover the Vent and Avoid Metal Foil:
- Do not cover the vent during use.
- Avoid covering any part of the microwave with metal foil.
Never Use the Microwave with the Door Open:
- Always ensure the door is securely closed before use.
Immediate Action in Case of Fire:
- Turn off power, unplug, and keep the door closed if a fire occurs.
Remember these measures for a hassle-free microwave cooking experience!
Common Misconceptions About Microwaves Cooking
Let’s clear up some common misunderstandings about cooking with a microwave:
Radiation leakage
- Myth: People often worry that microwaves leak harmful radiation.
- Fact: Microwaves use a type of radiation called non-ionizing radiation to cook food. Unlike ionizing radiation (like x-rays), which can be harmful, non-ionizing radiation is like what your TV or radio emits. It does not cause cancer, and the waves stay safely within the microwave’s metal walls and windows. So, don’t worry—your microwave won’t give you cancer!
Nutrient loss
- Myth: Some people believe that microwaving food causes significant nutrient loss.
- Fact: While all cooking methods can lead to some nutrient loss, microwaving is generally gentler than others. It preserves more nutrients compared to boiling or frying. So, your microwave isn’t secretly zapping away vitamins—it’s a safe way to cook!
Radiation effects on food
- Myth: Microwaving makes food radioactive.
- Fact: Not true! Microwaves heat food by exciting water molecules, not by making it radioactive.
Which Cookware / Utensil is Best for Microwave Cooking?
Ensuring safety with the right utensils for microwave use:
Glass Containers:
- Excellent for microwave cooking, safe, non-reactive, and can withstand high temperatures.
- Opt for glass containers with microwave-safe lids for reheating or direct cooking.
Ceramic Dishes:
- Microwave-safe, but ensure glaze or paint used is also microwave-safe.
- Avoid dishes with metallic accents to prevent sparks.
Microwave-Safe Plastics:
- Use plastics labeled as microwave-safe, with a squiggly line symbol at the bottom.
- Avoid regular plastics to prevent melting or releasing harmful chemicals.
Silicone Utensils:
- Microwave-safe and flexible, suitable for various cooking needs.
- Check the manufacturer’s instructions for temperature limits.
Avoid Metal and Foil:
- Never use metal utensils or containers to prevent sparks and microwave damage.
- Remove metal twist ties or staples from food packaging before microwaving.
Stainless Steel:
- Generally safe but not ideal for microwave cooking.
- Ensure it doesn’t touch the microwave’s sides.
Microwave-Safe Covers and Lids:
- Use microwave-safe covers to prevent splatters.
- Options include glass lids, microwave-safe plastic covers, or paper towels.
Follow these guidelines for safe and efficient microwave cooking. Enjoy your meals!
Pros and Cons of Microwave Cooking Technology
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of microwave technology:
Advantages of Microwave Cooking Technology:
Speed and Efficiency:
- Enables rapid cooking, saving time in busy lifestyles.
Energy Efficiency:
- Targets water molecules directly, reducing energy wastage.
Preservation of Nutrients:
- Shorter cooking times and lower temperatures preserve nutritional content.
Versatility:
- Effective for reheating, defrosting, and various cooking tasks.
Even Heating with Turntable:
- Turntables promote even heating, minimizing hotspots.
Disadvantages of Microwave Cooking Technology:
Uneven Heating in Some Cases:
- Certain foods or containers may result in uneven cooking.
Limited Browning and Crisping:
- Challenges achieving browning or crisping effects.
Restrictions on Cookware:
- Requires microwave-safe containers, limiting cookware options.
Potential Loss of Textural Quality:
- Some foods may experience texture changes during microwave cooking.
Safety Concerns:
- Safety features notwithstanding, concerns exist, emphasizing the need for regular maintenance.
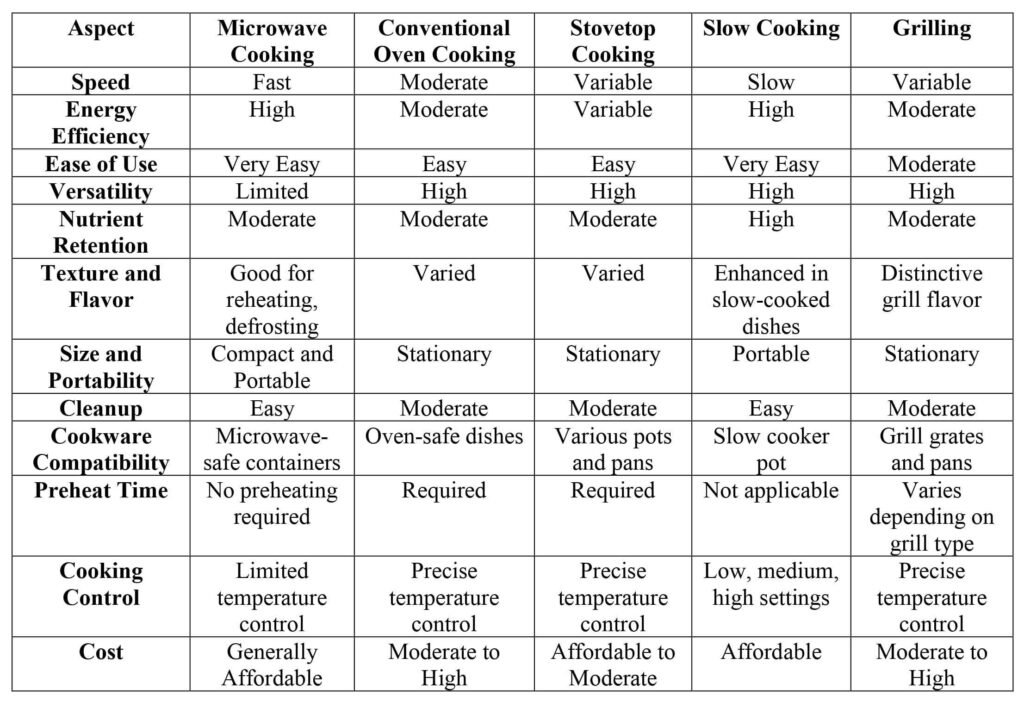
A Comparative Guide: Microwave Cooking vs. Other Cooking Methods
Explore the differences between microwave cooking and other cooking methods:
Keep in mind that the effectiveness of each cooking method depends on the specific dish and personal preferences.
Conclusion:
In Summary “How Does a Microwave Oven Heat Food?” helps you to understand the complicated science and safety steps involved in this amazing kitchen appliance. With this knowledge, you can make the most of your microwave cooking adventures.
Remember: Microwaves are not just for reheating – they’re also time machines that transport you from hunger to satisfaction in seconds!
FAQs about Microwave Cooking
Do Microwaves Kill Nutrients?
However, microwave cooking is one of the least likely forms of cooking to damage nutrients. That’s because the longer food cooks, the more nutrients tend to break down, and microwave cooking takes less time.
Are microwaves bad for your health?
Microwaves are non-ionizing radiation, so they do not have the same risks as x-rays or other types of ionizing radiation. But, microwave radiation can heat body tissues the same way it heats food. Exposure to high levels of microwaves can cause skin burns or cataracts.
Is Microwaved Food Safe to Eat?
Microwaved food is safe to eat. The radiation emitted by microwaves is non-ionizing, which means it doesn’t alter the chemical makeup of your food or make it radioactive. The World Health Organization confirms that there’s no harm in using microwaves for cooking.
However, some concerns remain, such as nutrient loss. Microwaving can reduce certain nutrients in vegetables, but the impact varies depending on factors like cooking time and water content.
Can Microwaving Cause Radiation Exposure?
Microwaved food is safe to eat. The radiation emitted by microwaves is non-ionizing, which means it doesn’t alter the chemical makeup of your food or make it radioactive. It doesn’t make your food radioactive or alter its chemical composition. However, some concerns remain, such as nutrient loss. Microwaving can reduce certain nutrients in vegetables, but the impact varies depending on factors like cooking time and water content.
Are Microwaves Energy-Efficient?
Microwaves are highly energy-efficient. They heat food directly, wasting less energy compared to conventional ovens. Here is a comparison:
Microwave: The average energy draw per hour is 1,200 watts, costing about $74 per year if used for 365 hours3.
Gas Oven: Uses significantly more energy (7,000 BTUs), costing around $146 per year.
Electric Oven: Consumes even more energy (3,000 watts), costing approximately $182 annually.
Having any queries? – Do reach us at info@scivoyage.com