Introduction:
5G technology represents the fifth generation of mobile network technology, it is offering faster speeds, lower latency, and more reliable connections compared to its predecessors. The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet.
This article explores how does 5G technology Enhance the Internet of Things – IoT, enabling more efficient and innovative applications across various industries.
What is IoT?
Definition of IoT
The Internet of Things refers to the network of physical objects—or “things”—embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies, to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet.
Historical Background and Evolution
The concept of IoT has been around for decades, but it started gaining traction in the early 2000s. Kevin Ashton, co-founder of the Auto-ID Center at MIT, coined the term “Internet of Things” in 1999. Since then, advancements in wireless technology, data analytics, and cloud computing have propelled IoT into mainstream consciousness.
Key Components of IoT Systems
- Sensors: These gather data from the environment, such as temperature, humidity, or motion.
- Connectivity: The data collected by sensors needs to be transmitted to a central location for processing, usually via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks.
- Data Processing: Once the data reaches cloud servers or edge devices, it’s processed to extract meaningful information.
- User Interface: This is the component that allows users to interact with the IoT system, such as through a smartphone app or web interface.
Importance of Both Technologies in Modern Life
Both 5G and IoT are revolutionizing the way we interact with technology. 5G brings the promise of ultra-fast connectivity, while IoT connects everyday devices, making them “smart” and capable of seamless communication.
Understanding 5G Technology
Definition of 5G Technology
5G is the next-generation mobile network technology designed to significantly improve the speed and responsiveness of wireless networks.
Key Features of 5G
- High Speed and Low Latency: 5G offers blazing-fast internet speeds and extremely low latency, enabling real-time communication between devices.
- Enhanced Capacity and Connectivity: 5G can support a higher number of connected devices simultaneously, making it ideal for densely populated areas and large-scale IoT networks.
- Improved Reliability and Efficiency: With advanced technologies, 5G ensures more stable and efficient connectivity, even under heavy network loads.
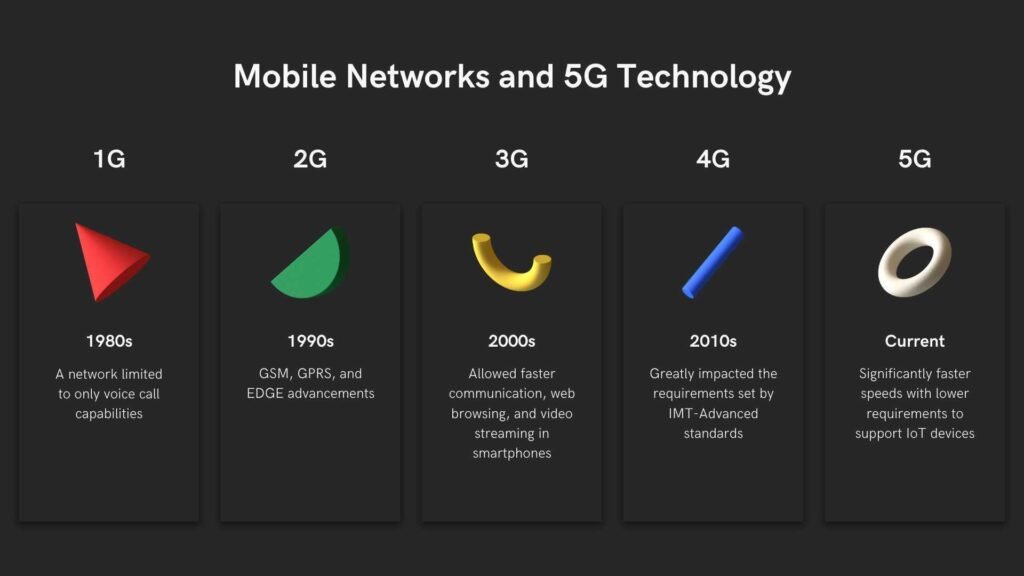
Comparison with Previous Generations
- 1G: Refers to the first generation of cellular network (wireless) technology.
- 2G: Significantly more efficient use of the radio frequency spectrum enabling more users per frequency band, like data services for mobile, starting with SMS text messages then expanding to Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS).
- 3G: Brought mobile email and basic internet browsing.
- 4G: Increased speeds suitable for streaming video and faster internet access.
- 5G: Offers speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G, with lower latency and the ability to handle more devices at once.
The Synergy Between 5G and IoT
How 5G and IoT Complement Each Other ?
5G and IoT are like a match made in tech heaven. 5G’s high-speed, low-latency network is perfect for the vast amounts of data that IoT devices generate.
Benefits of Integrating 5G with IoT
- Enhanced Communication Between Devices: 5G ensures devices can communicate rapidly and effectively, even in large numbers.
- Greater Data Transfer Speeds: With 5G, the data from IoT devices can be transferred almost instantaneously.
- Improved Real-Time Data Processing: 5G helps IoT systems process data in real-time, which is crucial for applications like autonomous driving and remote surgery.
Other Benefits of IoT and 5G
The other benefits of IoT and 5G technology is like:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Automation and data-driven insights can streamline processes.
- Enhanced Data-Driven Decision Making: Real-time data aids in making informed decisions.
- Improved Quality of Life: Smart homes and wearable devices add convenience and monitor health.
- Cost Savings in Various Sectors: Reduces wastage and operational inefficiencies.
Also read – Top 5 Examples of Cloud Computing
Key Enhancements 5G Brings to IoT
Speed and Bandwidth
- Faster Data Transmission Rates: 5G allows for quicker data uploads and downloads, essential for handling large volumes of IoT data.
- Support for More Devices Simultaneously: 5G supports many more connected devices, making it easier to scale IoT systems.
Latency Reduction
- Real-Time Responsiveness: Low latency means devices respond in real time, which is essential for critical applications like remote surgery.
- Critical for Applications Like Autonomous Vehicles and Remote Surgery: These applications require split-second decisions, which 5G enables with its low latency.
Network Slicing
- Customizable Network Configurations for Specific Needs: Network slicing allows portions of the 5G network to be tailored for specific applications, enhancing efficiency and performance.
- Enhanced Security and Reliability for Sensitive IoT Applications: With dedicated network slices, sensitive data can be more securely and reliably managed.
Massive Device Connectivity
- Ability to Support a Massive Number of IoT Devices: 5G’s increased capacity can handle the growing number of IoT devices across various applications.
- Benefits for Smart Cities and Industrial IoT: From managing traffic flows to monitoring industrial equipment, 5G’s capacity benefits large-scale IoT implementations.
Industry-Specific Impacts of 5G on IoT
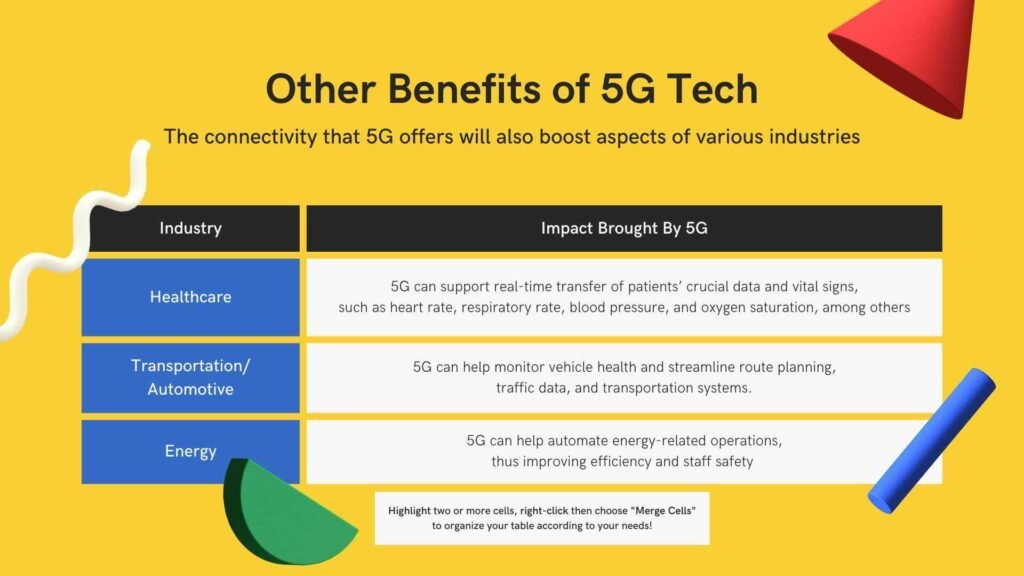
Healthcare
- Remote Patient Monitoring and Telemedicine: 5G enables real-time health monitoring and virtual consultations, improving healthcare access and outcomes.
- Real-Time Health Data Analytics: Instantaneous data transfer and analysis can lead to faster and more accurate diagnoses and treatments.
Manufacturing
- Smart Factories and Automation: Enhanced connectivity supports more sophisticated automation and communication between factory devices.
- Predictive Maintenance and Supply Chain Optimization: Real-time data helps predict equipment failures and optimize the supply chain, reducing downtime and costs.
Transportation
- Autonomous Vehicles and Traffic Management: 5G’s low latency and real-time data processing are crucial for the safe operation of autonomous vehicles and efficient traffic management.
- Enhanced Logistics and Fleet Management: With real-time tracking and data analysis, logistics and fleet management become more efficient.
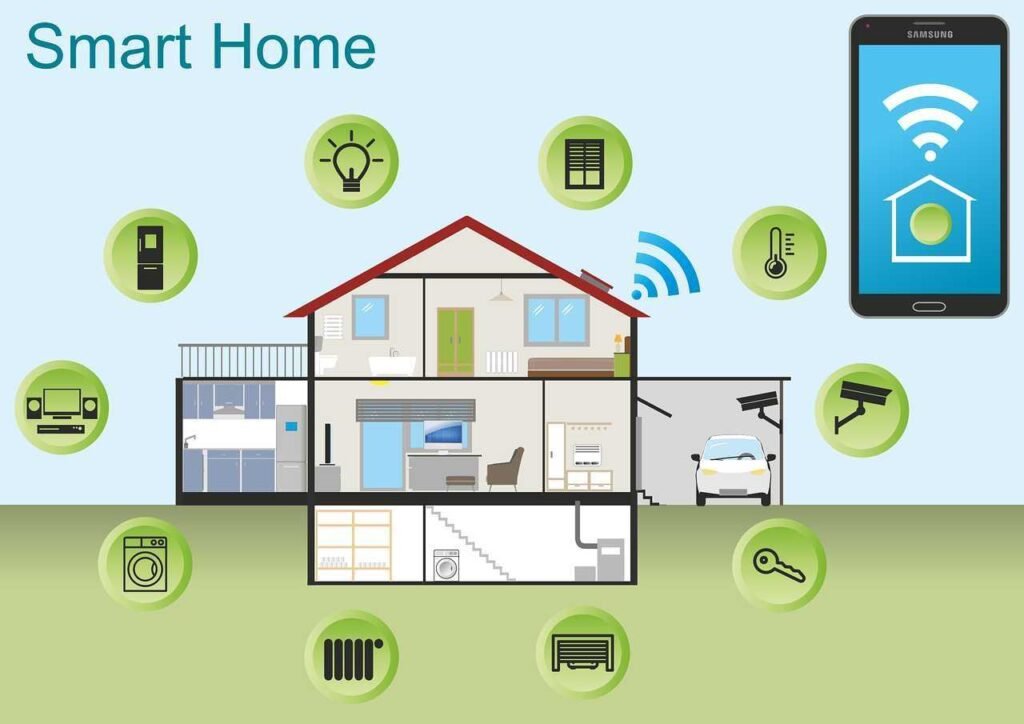
Smart Cities and Home
- Improved Public Safety and Emergency Response: Real-time data from connected devices can enhance public safety measures and improve emergency response times.
- Efficient Energy Management and Infrastructure: 5G-enabled IoT systems can optimize energy use and manage infrastructure more effectively.
Challenges and Considerations
Security Concerns
- Addressing Vulnerabilities in 5G and IoT Networks: Both 5G and IoT networks present new security challenges that need to be addressed to protect against cyber threats.
- Strategies for Enhancing Security: Implementing robust encryption, authentication, and regular security updates can help mitigate risks.
Infrastructure and Deployment
- Challenges in Implementing 5G Infrastructure: Deploying 5G requires significant investment in new infrastructure, like small cells and fiber optic cables.
- Costs and Regulatory Considerations: The cost of deployment and navigating regulatory requirements can be substantial hurdles.
Interoperability
- Ensuring Compatibility Between Different IoT Devices and Platforms: Interoperability between different devices and platforms is crucial for a seamless IoT ecosystem.
Also read – The Future of Artificial Intelligence in India
Future Outlook
Potential Advancements in 5G and IoT Technologies
Expect continuous improvements in network capabilities and device functionalities.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Innovations like AI integration with IoT and advancements in 5G technology are on the horizon.
Long-Term Impact on Society and Economy
The synergy between 5G and IoT is poised to transform industries, improve quality of life, and stimulate economic growth.
Conclusion
Recap of the Key Points Discussed
5G brings high speed, low latency, improved capacity, and reliability, which significantly enhance the capabilities of IoT.
Emphasis on the Transformative Potential of 5G in Enhancing IoT
The combined power of 5G and IoT holds immense promise for revolutionizing various industries and improving everyday life.
Final Thoughts on the Future of 5G and IoT
As these technologies continue to evolve, they will pave the way for even more innovative applications, shaping the future in exciting, unforeseen ways.
Having any queries? – Do reach us at info@scivoyage.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does 5G technology enhance the internet of things Accenture?
Thanks to 5G technology, the Internet of Things (IoT) works better because it offers faster data speeds and lower latency. This means data can be sent and received much more quickly, which improves real-time monitoring.
How does 5G technology enhance the internet of things IoT brainly?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of connected devices and sensors that gather and share data about their environment. 5G technology improves the IoT by offering faster data speeds and lower latency, allowing data to be sent and received more quickly with less delay.
What is the role of 5G wireless networks in the Internet of Things IoT?
The GSMA anticipates that early deployments of 5G will provide high-speed, low-latency, reliable, and secure mobile broadband. Over time, a vast number of IoT devices will connect to 5G networks, offering support for ultra-reliable and low-latency communications.
Why is it called Internet of Things?
Kevin Ashton, who created the concept of the Internet of Things (IoT), had worked in supply chain optimization. He wanted to get the attention of top management with a new and innovative technology called RFID. Since the internet was the hottest technology in 1999, he decided to name his presentation “Internet of Things.”
Who is the father of IoT?
Father of Internet of Things – Kevin Ashton
Kevin Ashton is a British-born technology pioneer recognized as the Father of the Internet of Things.
















11 thoughts on “How Does 5G Technology Enhance the Internet of Things (IoT)”
you could have an excellent weblog right here! would you prefer to make some invite posts on my blog?
Thanks for shening. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article. https://www.binance.com/ur/register?ref=WTOZ531Y
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.info/it/join?ref=S5H7X3LP
Today, I went to the beachfront with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but I had to tell someone!
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.