Introduction:
The Internet of Things (IoT) has become a buzzword recent year, and for good reason. From smart homes to connected cars, IoT is transforming the way we live and work. what exactly is IoT, and why is it so important? In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the world of IoT, its origins, how it works, its various applications, and what the future holds.
What is IoT?
Definition of IoT
The Internet of Things refers to the network of physical objects—or “things”—embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies, to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet.
Historical Background and Evolution
The concept of IoT has been around for decades, but it started gaining traction in the early 2000s. Kevin Ashton, co-founder of the Auto-ID Center at MIT, coined the term “Internet of Things” in 1999. Since then, advancements in wireless technology, data analytics, and cloud computing have propelled IoT into mainstream consciousness.
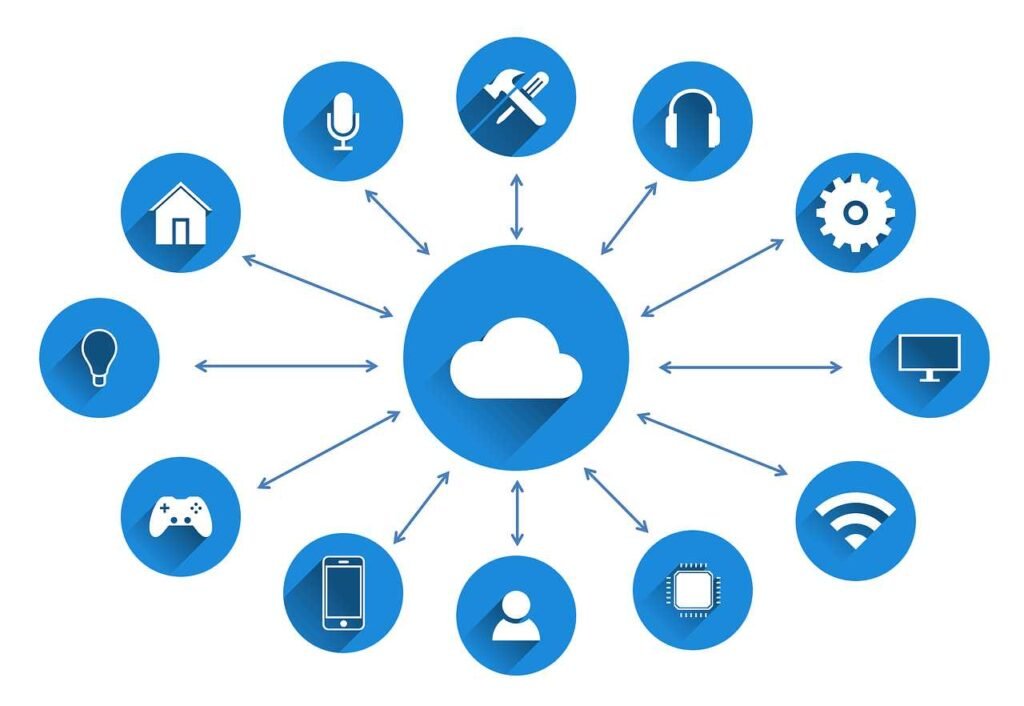
Key Components of IoT Systems
- Sensors: These gather data from the environment, such as temperature, humidity, or motion.
- Connectivity: The data collected by sensors needs to be transmitted to a central location for processing, usually via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks.
- Data Processing: Once the data reaches cloud servers or edge devices, it’s processed to extract meaningful information.
- User Interface: This is the component that allows users to interact with the IoT system, such as through a smartphone app or web interface.
How IoT Works ?
Basic Architecture of IoT Systems
An IoT system is typically composed of four layers:- Sensors/Devices
- Networking/Connectivity
- Data Processing
- User Interface

Communication Protocols
Different communication protocols are used based on the requirements of the IoT system:- Wi-Fi: Ideal for devices that need high data rates.
- Bluetooth: Used for short-range communication.
- Zigbee: Suited for low-power, low-data rate applications like home automation.

Data Collection, Processing, and Analysis
Once data is collected by sensors, it is transmitted to cloud-based servers where it is processed using algorithms and analytics tools to convert raw data into actionable insights.Examples of IoT Devices and Ecosystems
- Smart Thermostat: Adjusts home temperature based on user preferences.
- Wearable Fitness Tracker: Monitors physical activity and health metrics.
- Connected Cars: Provide features like remote start and vehicle diagnostics.
Applications of IoT
Smart Homes
- Home Automation: Controlling lighting, heating, and security systems remotely through a smartphone app.
- Voice-Activated Assistants: Devices like Amazon Alexa and Google Home can perform tasks based on voice commands.
Healthcare
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Enables continuous health monitoring of patients with chronic conditions.
- Wearable Health Devices: Fitness trackers and smartwatches help users keep a tab on their health metrics.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
- Predictive Maintenance: Monitors machinery to predict failures before they occur.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracks goods in real-time from production to delivery.
- Smart Manufacturing: Uses IoT to optimize the manufacturing process.
Smart Cities
- Traffic Management: Analyzes traffic data to control traffic signals and reduce congestion.
- Waste Management: Sensors in trash bins alert when they are full and need to be emptied.
- Public Safety: Surveillance cameras and disaster management systems are enhanced with IoT.
Agriculture
- Precision Farming: Uses IoT to monitor soil conditions and optimize crop yields.
- Livestock Monitoring: Tracks the health and location of livestock.
- Automated Irrigation Systems: Adjusts watering schedules based on soil moisture levels.
Benefits of IoT
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Automation and data-driven insights can streamline processes.
- Enhanced Data-Driven Decision Making: Real-time data aids in making informed decisions.
- Improved Quality of Life: Smart homes and wearable devices add convenience and monitor health.
- Cost Savings in Various Sectors: Reduces wastage and operational inefficiencies.
Also read – Top 5 Examples of Cloud Computing
Challenges and Risks of IoT
- Security Concerns: Data breaches and hacking are significant risks.
- Privacy Issues: The massive amounts of data collected can be a privacy concern.
- Standardization and Interoperability: Different manufacturers use different protocols, making integration a challenge.
- Scalability and Infrastructure: As more devices get connected, the infrastructure needs to be capable of handling the load.
Future Trends in IoT
- Edge Computing: Processes data closer to where it is generated, reducing latency.
- 5G and Its Impact on IoT: 5G will enable faster and more reliable connectivity.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Enhances the capabilities of IoT systems to make smarter decisions.
- Expansion of IoT in Various Sectors: More industries are finding ways to incorporate IoT to improve their operations.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Smart City Project
A smart city project in Barcelona uses IoT for traffic management, waste management, and improving public safety, making the lives of its residents more comfortable and secure.
Case Study 2: Healthcare IoT Application
A remote patient monitoring system in a hospital tracks vital signs in real-time, enabling timely interventions and reducing hospital readmission rates.
Case Study 3: Industrial IoT in Manufacturing
A car manufacturing plant uses IoT for predictive maintenance, drastically reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Also read – The Future of Artificial Intelligence in India
Conclusion
The Internet of Things has journeyed from a novel concept to an integral part of our lives and industries. It is revolutionizing various industries by making systems more efficient, data-driven, and user-friendly. From smart homes to healthcare and industrial applications, the potential of IoT to transform our daily lives is immense.
Additional Resources
- IoT Agenda: A comprehensive resource for IoT news and trends.
- Recommended Reading: “The Internet of Things: Key Applications and Protocols“ by Olivier Hersent.
- IoT Events: Check out the annual IoT Tech Expo.
Having any queries? – Do reach us at info@scivoyage.com
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is it called Internet of Things?
Kevin Ashton, who created the concept of the Internet of Things (IoT), had worked in supply chain optimization. He wanted to get the attention of top management with a new and innovative technology called RFID. Since the internet was the hottest technology in 1999, he decided to name his presentation “Internet of Things.”
Who is the father of IoT?
Father of Internet of Things – Kevin Ashton
Kevin Ashton is a British-born technology pioneer recognized as the Father of the Internet of Things.What is the purpose of IoT?
The primary goal of IoT is to link any device or object to the internet, enabling them to gather and exchange data, as well as be monitored and controlled remotely.
What is IoT and its examples?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a technology that allows us to incorporate a device into previously lifeless objects. This gadget can measure environmental characteristics, create pertinent data, and send it across a communication network.
What is IoT used for today?
IoT is most prevalent in industrial, transportation, and utility businesses, where sensors and other IoT devices are widely used.
However, it also has useful applications for firms in the agricultural, infrastructure, and home automation industries, motivating many to start on a digital transformation path.









10 thoughts on “The Evolution of Internet of Things (IoT)”
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.