Introduction
For ages, humanity has been fascinated by the vastness of our Milky Way Galaxy. Understanding the number of solar systems not only piques our interest in our cosmic neighborhood but also provides a framework for future discoveries.
In this blog article, we will look at what makes up a solar system, explore the structure of our Milky Way, and discuss the methods and challenges of determining the number of solar systems in a galaxy.
Also read – Top 15 Space Agencies in the World for 2024
What is a Solar System?
Definition of a Solar System
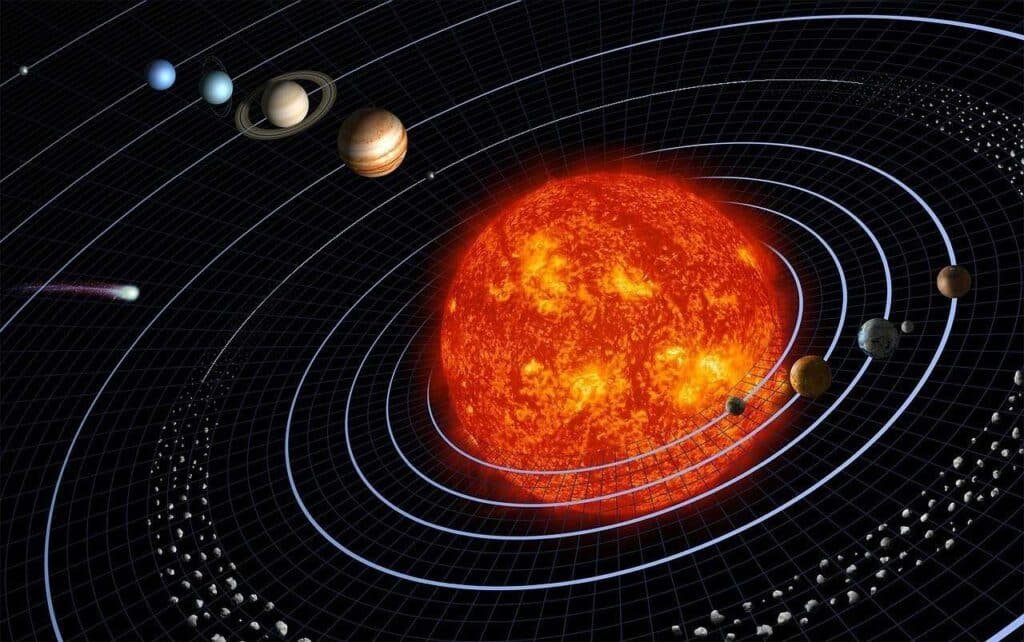
A solar system is defined as a star and all the celestial bodies that orbit around it. For example, our Solar System includes the Sun, Earth, Mars, the Moon, and other planets.
Components of a Solar System
- Star: The central celestial body, like our Sun.
- Planets: Bodies that orbit the star, such as Earth and Mars.
- Moons: Natural satellites, like our Moon.
- Asteroids and Comets: Smaller celestial objects that also orbit the star.
The Milky Way Galaxy: Our Cosmic Neighborhood
Introduction to the Milky Way
The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy that contains our Solar System. It’s our cosmic home, housing billions of stars, many of which likely have their own solar systems.
Structure of the Milky Way
- Galactic Center: The bustling heart of the Milky Way.
- Spiral Arms: Regions where many stars, including our Sun, reside.
- Halo: The spherical region surrounding the galaxy.
Estimating the Number of Solar Systems in the Milky Way
Why is this Estimation Challenging?
Estimating the number of solar systems in the Milky Way is a difficult task. The immense size of the galaxy and the vast number of stars present significant challenges. Additionally, our current technology and observation methods have limitations.
Methods of Estimation
- Stellar Surveys: Cataloging stars and their characteristics.
- Exoplanet Detection: Discovering planets orbiting other stars.
- Statistical Models: Using existing data to predict the number of solar systems.
How Many Solar Systems Are There in the Milky Way?
Current Estimates
Scientists estimate that there could be tens of billions of solar systems in the Milky Way. This number is based on the observation of stars and the detection of exoplanets (planets outside our Solar System). As technology improves and more exoplanets are discovered, these estimates become more accurate. Current research and observations suggest that a significant percentage of stars host planets, indicating a vast number of solar systems in our galaxy.
Influential Factors
Star Types:
Different stars have varying probabilities of hosting planets. For example, stars similar to our Sun (G-type stars) are more likely to have planets in their habitable zones where conditions might support life. Red dwarfs, the most common type of star in the Milky Way, also frequently have planets, though the conditions on these planets can be very different from those around Sun-like stars.
Planetary Formation:
Understanding how planets form around stars is crucial. Planets form from the dust and gas that surround a new star in a disk shape. The process and conditions needed for planet formation can vary, influencing how many planets are likely to form around different types of stars.
Technological Advancements:
Improved telescopes and detection methods have greatly enhanced our ability to find and study exoplanets. Techniques like the transit method (observing a planet as it passes in front of its star) and the radial velocity method (detecting wobbles in a star’s motion due to gravitational pull from orbiting planets) have led to the discovery of thousands of exoplanets.
Also read –List of ISRO Space Centers in India
Notable Solar Systems in the Milky Way
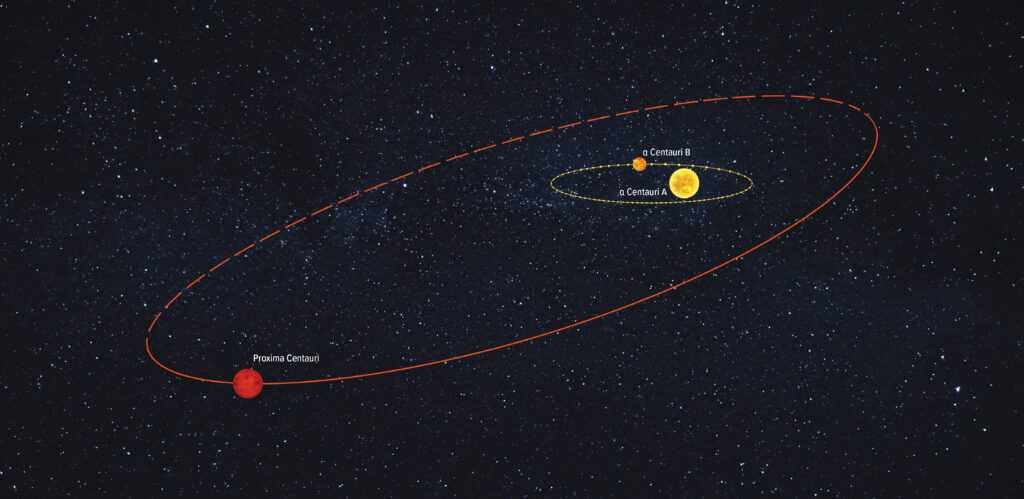
Proxima Centauri System:
This is the closest known exoplanetary system to us, just over 4 light-years away. It features Proxima b, a planet located in the habitable zone of the red dwarf Proxima Centauri. Proxima b’s potential habitability makes it a key target for studying conditions that might support life.
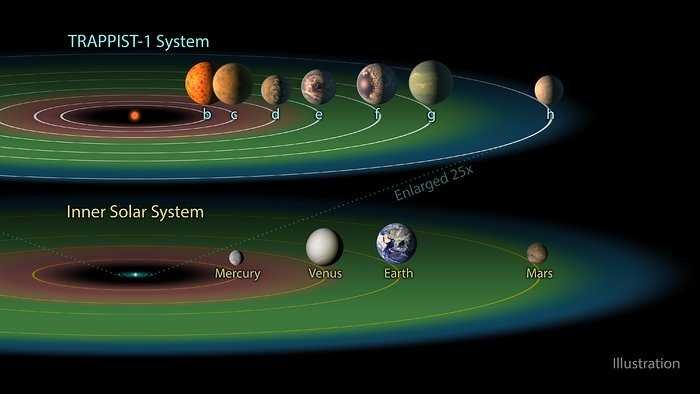
TRAPPIST-1 System:
The TRAPPIST-1 system, about 39 light-years away, is notable for having seven Earth-sized planets, three of which are in the habitable zone where liquid water could exist. This system is fascinating because it offers multiple targets for studying potentially habitable environments outside our Solar System.
Also read – Top 5 Private Space Companies in India
Significance of Discovering Various Solar Systems
Planetary Formation and Evolution:
By studying different solar systems, scientists can learn more about how planets form and evolve. This knowledge helps us understand our own Solar System’s history and development.
Potential for Life:
Discovering solar systems with planets in habitable zones increases the chances of finding extraterrestrial life. By identifying planets with conditions similar to Earth, we can narrow down the search for life beyond our planet.
Technological Advancements:
The pursuit of discovering and studying exoplanets drives the development of new technologies, such as more powerful telescopes and advanced detection methods. These innovations can have broader applications in science and industry.
Challenges in Identifying Solar Systems
Distance:
Even the nearest solar systems are light-years away, making them difficult to observe directly. The vast distances involved pose significant challenges for detailed study and exploration.
Detection Limitations:
Current technology sometimes struggles with detecting smaller exoplanets, especially those that are Earth-sized or smaller. Many detection methods are biased toward finding larger planets or those very close to their stars.
Interstellar Interference:
Cosmic dust, gas, and other celestial phenomena can obscure our view of distant stars and planets. This interference makes it harder to gather clear and accurate data about other solar systems.
The Future of Solar System Exploration
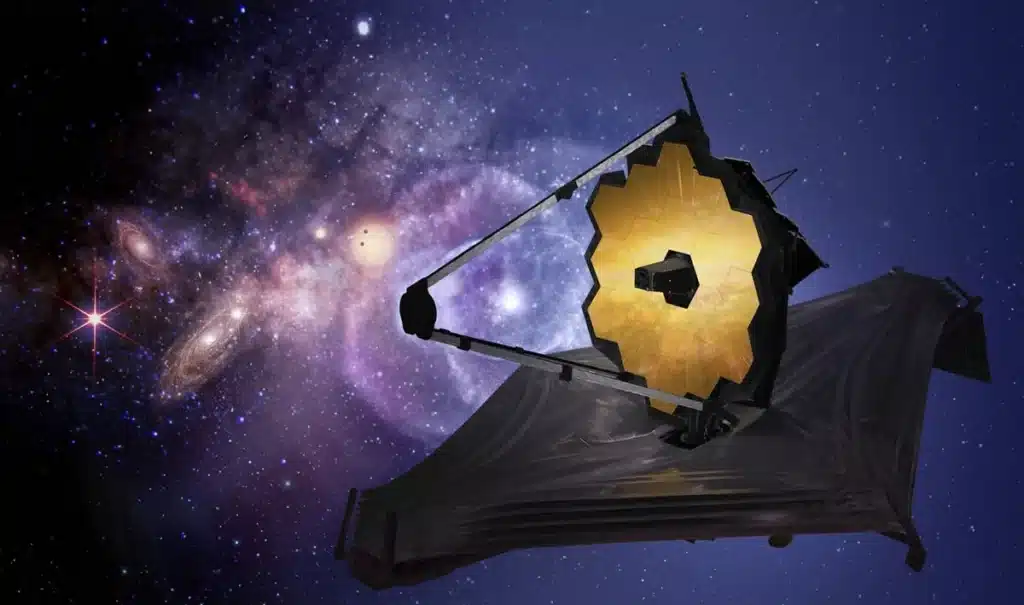
James Webb Space Telescope (JWST):
Scheduled to provide unprecedented detail of distant solar systems, the JWST will enable scientists to study the atmospheres of exoplanets, analyze their compositions, and search for signs of habitability or even life.

AI and Machine Learning:
These technologies are enhancing our capabilities to sift through enormous datasets for potential discoveries. AI can help identify patterns and signals that might indicate the presence of exoplanets, speeding up the discovery process.
Interstellar Probes:
Concepts like Breakthrough Starshot aim to send microprobes to nearby solar systems like Proxima Centauri. These probes would travel at a fraction of the speed of light, potentially providing direct data from other solar systems within a few decades.
By continuing to explore and understand our galaxy’s solar systems, we not only expand our knowledge of the universe but also drive technological and scientific advancements that benefit humanity.
Also read – List of Moon Landed Countries
Conclusion
We’re on an exciting journey to discover how many solar systems exist in our galaxy. Each new finding not only teaches us more but also inspires us to learn about the universe. As technology improves, so does our ability to uncover the mysteries of countless solar systems in our Milky Way and beyond.
By studying our own Solar System, understanding the Milky Way Galaxy, and exploring many potential solar systems, we’re expanding our knowledge of the universe. This journey satisfies our curiosity and sets the stage for future cosmic exploration.
Our exploration of the galaxy has only just begun. Let’s keep looking up at the stars, because each one could lead to a new discovery. The universe is vast and ready to reveal its secrets to those who seek them. Happy star-gazing, fellow explorers!
Frequently Asked Questions
How many solar systems have been discovered in the Milky Way?
While thousands of exoplanets have been found, the exact number of solar systems remains a subject of research.
What is the most Earth-like exoplanet discovered so far?
Proxima b and planets in the TRAPPIST-1 system are among the most Earth-like.
How do scientists detect exoplanets?
Methods include transit photometry, radial velocity, and direct imaging.
How many Suns are in the Milky Way galaxy?
Our galaxy, the Milky Way, has at least 300 billion stars. When a star is at the center of a planetary system like Earth and its orbiting planets, we call it a “Sun.”
Which planet is the hottest?
Venus
Venus holds this title because of its strong greenhouse effect, similar to Earth’s. Due to this effect, Venus has the highest temperatures in our solar system, with surface temperatures reaching around 465°C!
Having any queries? – Do reach us at info@scivoyage.com